Maths
Autumn 1
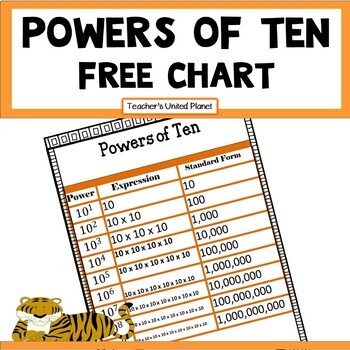
Power of 10 is the number 10 multiplied by itself by the number of times indicated.
Negative numbers
Numbers don't just stop at zero. When you count backwards from zero, you go into negative numbers.
Positive numbers are more than zero: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc.
Negative numbers are less than zero: -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, etc.
A number line can be used to order negative and positive numbers.
Zero, 0, is neither positive nor negative.
Click on the click below for further understanding.
Using place value charts
You can use place value charts to help divide by 10, 100 and 1000. This helps you to see how the digits change in value.
A trick to help you remember how many places the digits need to move is by looking at the zeros in 10, 100 and 1000.
For example, there are 3 zeros in 1000, so you need to move the digits 3 places to the right to divide by 1000.
- x10 - 1 zero move 1 place
- x100 - 2 zeros move 2 places
- x1000 - 3 zeros move 3 places
What is a common factor?
-
A is a whole number which is a of two or more numbers.
-
The (HCF) is the greatest factor that will divide into two or more numbers.
-
The (LCM) is the smallest that is common to two or more numbers.
What is an integer?
An integer is a whole number that can be negative or positive (but cannot be both at the same time).

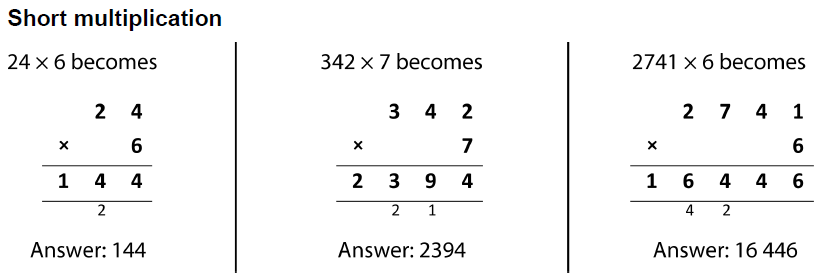
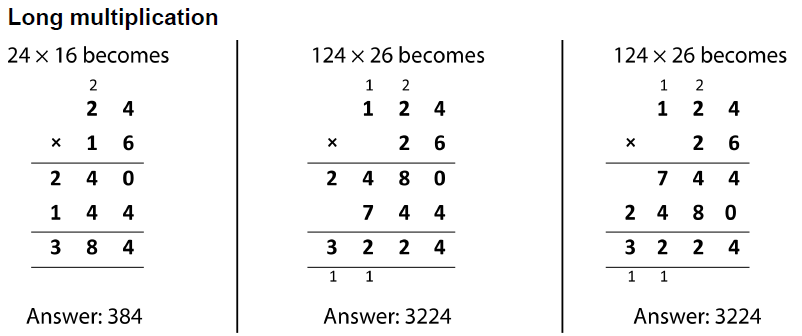



![Short Division [Bus Stop Method] | Teaching Resources](https://d1e4pidl3fu268.cloudfront.net/71a5d70d-1898-4607-8179-663b81000f37/ScreenShot20161209at205554.crop_268x201_0%2C19.preview.png)
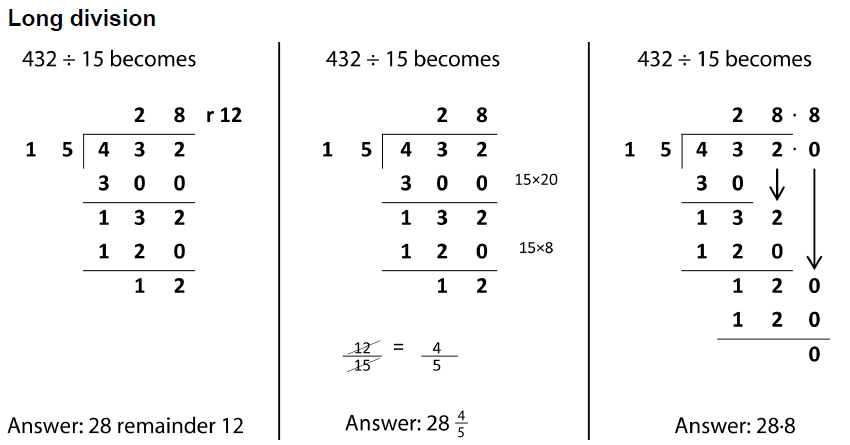
Short division is also known as the bus stop method and is often used to divide large numbers.
Division is sharing things out or working out how many times one number goes into another. Division is the of multiplication.
When doing short division, it can be useful to know your times tables. It is also important to be able to work out if values do not divide

Autumn 2
In Fractions, the children wiil be learning the following:
- Use common factors to simplify fractions; use common multiples to express fractions in the same denomination
- Compare and order fractions
- Add and subtract fractions with different denominators and mixed numbers, using the concept of equivalent fractions
- Multiplying / dividing simple pairs of proper fractions, writing the answer in its simplest form.
Common denominators / different denominators
It's easy to add and subtract fractions when the numbers on the bottom are the same.These are called the denominators It gets a little tricky when the denominators are different. Please see the small clips below for further understanding.



Multiplying/dividing fractions. Click Me ↓

Friday 18th November
Today the children spent their Maths lesson reseaching the famous English mathematician and Writer Ada Lovelace.
The children worked in pairs to find out the following:
- Why was she known as a mathematician?
- What was her input on the 'Difference Engine?
- Why was Ada's notes about the Analytical Engine were well received?
Fun Facts about Ada Lovelace
- As a child, Ada Lovelace was interested in flying. She made wings for herself out of different materials, including wire and paper, and wrote a book about her research.
- She became friends with several famous scientists and writers of the time, including Charles Dickens and Wheatstone, inventor of the telegraph.
- She had to publish her work under her initials, as women were not seen to be intellectual.
- The US department of defence computer language is named Ada. The British Computer Society awards the Ada Lovelace medal annually, and each October, Ada Lovelace Day recognizes women in maths, science and engineering.
Spring 1
This term, the children have worked exteremly hard understanding different types of fractions. Whether it be adding and subtracting or multiplying and dividing fraction, they have worked at a high standard.
Please see the work below.
All the children have worked amazing for the past 5 weeks and deserve a well earn rest.



Spring 2

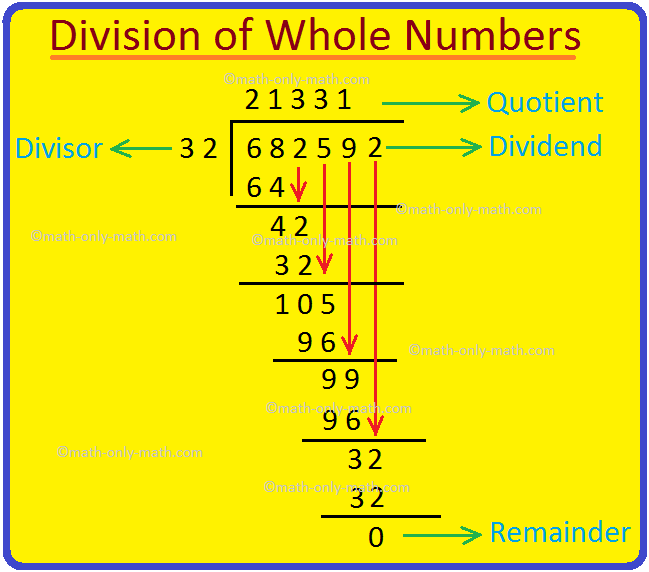
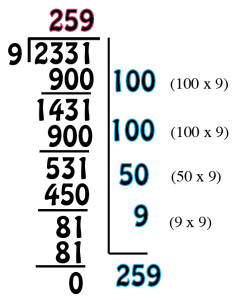
This week, the children will be looking at Division.
 Reedley Primary School
Reedley Primary School